International Projects
Collaborations and implementation of projects at international level.
Ongoing Projects
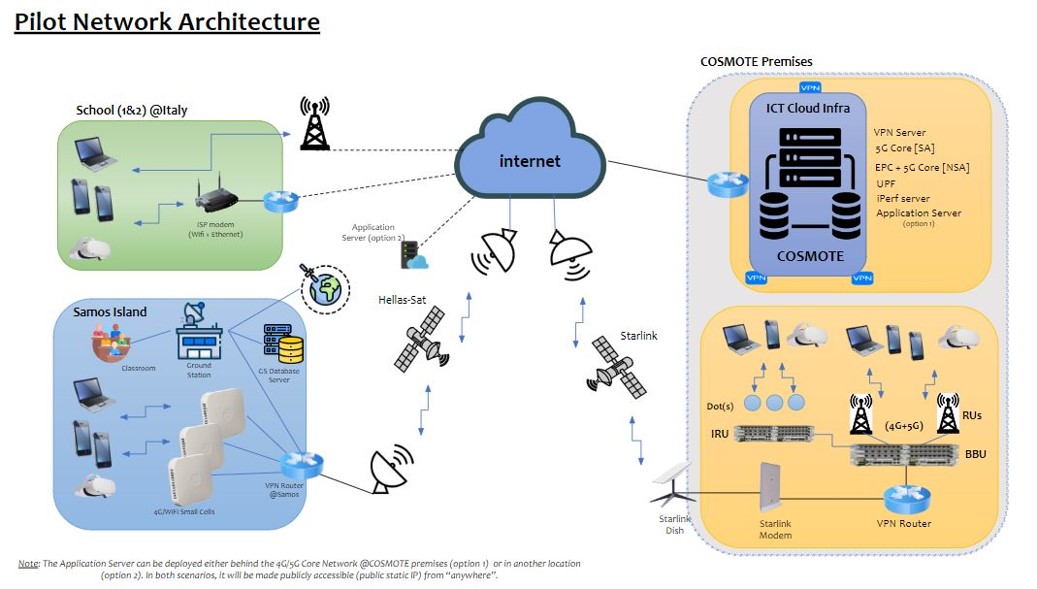
The project proposes a 5G-enabled, satellite-supported educational platform, that: provides an advanced school experience to students without access to advanced educational services; introduces space, human spaceflight and satellites as a hands-on educational topic; utilizes earth observation and satellite navigation services to implement a novel educational approach with the goal to increase student awareness on environmental issues.
The solution relies on an educational platform that supports hybrid educational schemes aiming to both facilitate a smooth transition to the post Covid-19 era that will prevent a learning crisis, but also to redesign the conventional learning and teaching processes with the scope of addressing issues that have been a subject of discussion for several years, like preventing dropouts or reducing the exclusion rates in education. The platform will provide a set of solutions concerning both the teaching and learning process that is based on emotional and cognitive learning analytics within the context of flipped learning in a virtual or hybrid educational scheme. The efficient design of the platform prerequisites the effective combination of the pedagogical aspects with emerging technologies, like artificial intelligence (AI) and virtual/augmented reality (VR/AR).
A main project goal is the student-teacher access assurance regardless of the school location, the house location of each individual and the current living conditions. As an example, we can consider remote Greek islands of the northeastern Aegean with no overall 5G connectivity, remote areas with no anticipated 5G coverage, and special-conditions areas (e.g., schools in refugee camps). The network of connectivity will be based on terrestrial technologies and 5G, while satellite through 5G backhauling can enable and support the required throughput at remote schools and areas (lacking 5G infrastructure).
The VR/AR service will be augmented by EO pictures (e.g., Airbus platform – https://oneatlas.airbus.com/home) to provide courses in Earth Observation. As examples, the syllabus will be enriched with (possibly real-time) imaging of environmental event progression (e.g., oil spills, wildfire events – raising student awareness), or crop monitoring as part of environmental studies. Additionally, effort will be made to extend the platform to offer the exceptional platform services to students with disabilities – utilizing Audio Visual technologies to assist them, and include them in the overall educational experience. In the following, educational platform use cases are presented. The platform is the outcome of the DiSTARS Erasmus+ KA2 project which is still running. It offers a synchronized integration of Art and STEM in the curriculum, simulating the ways in which subjects naturally connect in the real world. Combining scientific inquiry with artistic expression (e.g., visual and performing arts), storytelling, along with AR and VR technology, the DiSTARS platform is capturing the imagination of young students and provides them with opportunities for digital creative expression. Based on the outcome of the H2020 Stories of Tomorrow RIA project (2019-2021), DiSTARS provides innovative VR & AR interfaces that were validated by more than 3000 students all over Europe. It allows for various types of creations (e.g paintings, models, dioramas and constructions, 3D objects and landscapes, animations, science videos and even science theater plays) to be captured according to students’ scenarios and be integrated in their storylines.
Additionally, the platform enriches students’ experience by providing scaffolds and guidance while they are dealing with the issues that they consider quite difficult and complex to understand. The system offers different learning paths to support individual student’s conceptual change and understanding (videos, animations, 3D representations). In such a way students become more engaged in the learning process, and they realize that they have the possibilities to personalize the learning path to meet their own needs. The platform also supports teachers’ work by providing alternative learning paths for students who are facing difficulties in specific subjects under study. For example, a student has difficulties working with mathematical functions. On the other hand, the same student loves music and performs as a drummer in the school band. Teacher has the chance to design an alternative path to introduce the student to the mathematical concept by using music instruments and functions
A ground station monitoring facility (Earth Station – ES) able to communicate with various satellites in orbit will act as a server of satellite data for educational purposes. The data will be consumed by the proposed educational platform. Thus, students will be able to learn more about satellite orbits and satellite communication payload. For instance, they will be able to design their own mission to receive signals and/or images from real satellites orbiting in space. There will be two options regarding operation and control of the ES. In-situ operations where students will visit the building where the equipment is located and try to set up a monitoring and communication operation with various satellites in orbit and remote control over a fast and reliable 5G network.
The development of Governmental Satellite Communications (GOVSATCOM) is a key element of the Global Strategy for the European Union’s foreign and security policies. On the other hand, Cyprus is an island country that continuously has been in the epicenter of security, safety, and geopolitical events. GOVSATCOM is the cost-efficient and user-oriented infrastructure that aims to provide secure and highly available satellite communications to the governmental authorities – managed and controlled by the authorities in order to assure extended communication coverage, availability, seamless mobility, as well as secure transactions of graded information and message broadcasting of national importance. The GOVSATCOM has the national goal to exploit secure satcom to:
- Support crisis management operations under difficult conditions (e.g., maritime emergencies, refugee crises) and natural/man-made disaster (e.g., warfare, water contamination, earthquakes, hurricanes, and flash floods) in case of commercial/public network interruptions.
- Sustain surveillance (e.g., borders, natura 2000, national landmarks, and maritime surveillance), weather, environmental and structural monitoring, protection of critical infrastructures (e.g., coastline, dams, bridges, power stations, etc.), trafficability of maritime routes, as well as support defense missions and operations.
- Strengthen security and access controls (with respect to border control, flood warning, earthquake detection, early warning for possible fire disasters) and act as secure means for transaction of graded information and message broadcasting of national importance.
- Provide services to governmental and non-governmental aid agencies in areas of health, education, socioeconomic development, and e-government.
Within the framework of the ESA PECS 7 program, the consortium of Hellas sat, RHEA and University of Aegean plan to propose the implementation of a Cypriot governmental satellite communication system (CyCOM). The consortium will utilize its expertise to design, implement and deploy secure satellite communications customized to the needs and security requirements of the government, having as main scope and end project result the introduction and presentation to the Cypriot Government of a fully functional secure satellite network that can be maximally exploited for governmental applications.
ERMIS [Hellenic Cubesat Demonstration Mission] is a pathfinder demonstration of key space connectivity capabilities linked to Greece’s 200M€ national small satellite project using a constellation of small satellites. Coordinated by the National Kapodistrian University of Athens (NKUA) the consortium includes leading space, small satellite and IoT/communications entities OQ Hellas, University of Patras, University of the Aegean and the National Observatory of Athens. As the first Greek small satellite constellation, ERMIS will bring novel space communications (Low Earth Orbit 5G-IoT communication services, Inter-Satellite Link (ISL) and laser optical downlink), hyperspectral earth observation applications focused on national needs (e.g., precise agriculture) and small satellite technology capabilities for Greece and Europe, and create unprecedented new space capacities, synergies, and infrastructure in Greece.
The ERMIS mission consists of a constellation of three (3) advanced, 6U cubesats focused on demonstrating key communications/connectivity and earth observation technologies and applications, utilizing a mixture of existing Greek space technology such as communications (IoT/5G, ISL), CCSDS on-board data processing, state-of-the-art FPGA accelerators for hyperspectral image compression and optical channel-coding, attitude control tracking algorithms, laser optical communications demonstrating 1 Gbps downlink to the Helmos Optical Ground Station, hyperspectral imaging (5m GSD), associated EO applications and national space infrastructure for its ground segment. Launch of the ERMIS constellation is planned for the end of 2025.
The initiative underpins efforts – led by ESA on behalf of the Greek Ministry of Digital Governance – to expand the nascent space industry in Greece, enabling the digital transformation of society while creating jobs and generating prosperity, as part of the nation’s EU-funded Recovery and Resilience Facility. The ERMIS 4.8M€ project is funded by the European Union – NextGenerationEU and by the Greek Ministry of Digital Governance and is coordinated by the Department of Aerospace Science and Technology of the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens. The rest of the consortium is comprised of OQ Hellas, University of Patras – Department of Mechanical Engineering & Aeronautics, University of the Aegean – Department of Information and Communication Systems Engineering – Computer and Communication Systems Laboratory (https://ccsl.icsd.aegean.gr) and National Observatory of Athens.
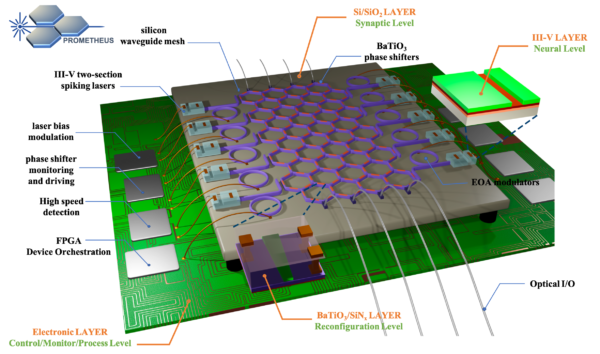
PROMETHEUS’ vision: is to shatter the boundaries between quantum and neuromorphic photonic processing and merge them into a uniform integrated platform. In particular, the PROMETHEUS’ photonic integrated chip (PIC) will be based on a highly dense silicon on insulator (SOI) Field Programmable Photonic Gate Array (FPPGA) synaptic layer, strengthened by nearly-zero power-consuming non-volatile barium titanate (BTO) phase shifters and co-integrated III-V lasers, that will form an ultra-fast spiking neural layer. Sophisticated packaging, will provide a disruptive, yet robust device able to unravel large-scale neuromorphic-quantum implementations, offering unprecedentedly low power consumption, processing speed and versatility to adapt to a wide pallet of applications.
PROMETHEUS’ multi-purpose photonic platform will be suitable for the exploration of emerging concepts such as spiking networks, reservoir computing, convolutional optical networks and quantum neural networks; aiming to address two key industry-driven applications: high-speed image processing for biomedical/industrial applications (cytometry/laser scanning) and optical signal processing at the network’s edge (signal equalization). Moving a step further, PROMETHEUS’ PIC will be also utilized as a physical root of trust, unlocking its use as a quantum random number generator (QRNG) module and as a cyber-secure photonic physical unclonable function (PUF). These two operations will provide a pivotal advantage to PROMETHEUS’ modules: to act as neuromorphic processors and at the same time, to provide hardware-based authentication and security features derived from quantum key.
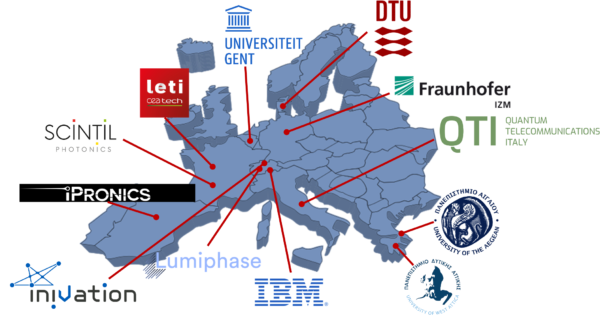
The University of the Aegean has the technical supervision of the entire project (technical management), while the IPRONICs company from Spain (coordinator), the University of Western Attica, the Technical University of Denmark DTU, the University of Ghent from Belgium, the QTI company from Italy, the CEA-LETI research center from France, the FRAUNHOFER IZM research center from Germany, the Scintil Photonics company from France, IBM from Switzerland, the Lumiphase company from Switzerland and the Inivation company from Switzerland, also participate in the project.
The role of the University of the Aegean is the design and characterization of photonic devices, the design and study of optical neural networks and their training, the use of devices as quantum cryptographic tools as well as the application of systems for ultra-fast image analysis.
The Technical Director of the project and Scientific responsible from the side of the University of the Aegean is Associate professor Charis Messaritakis.
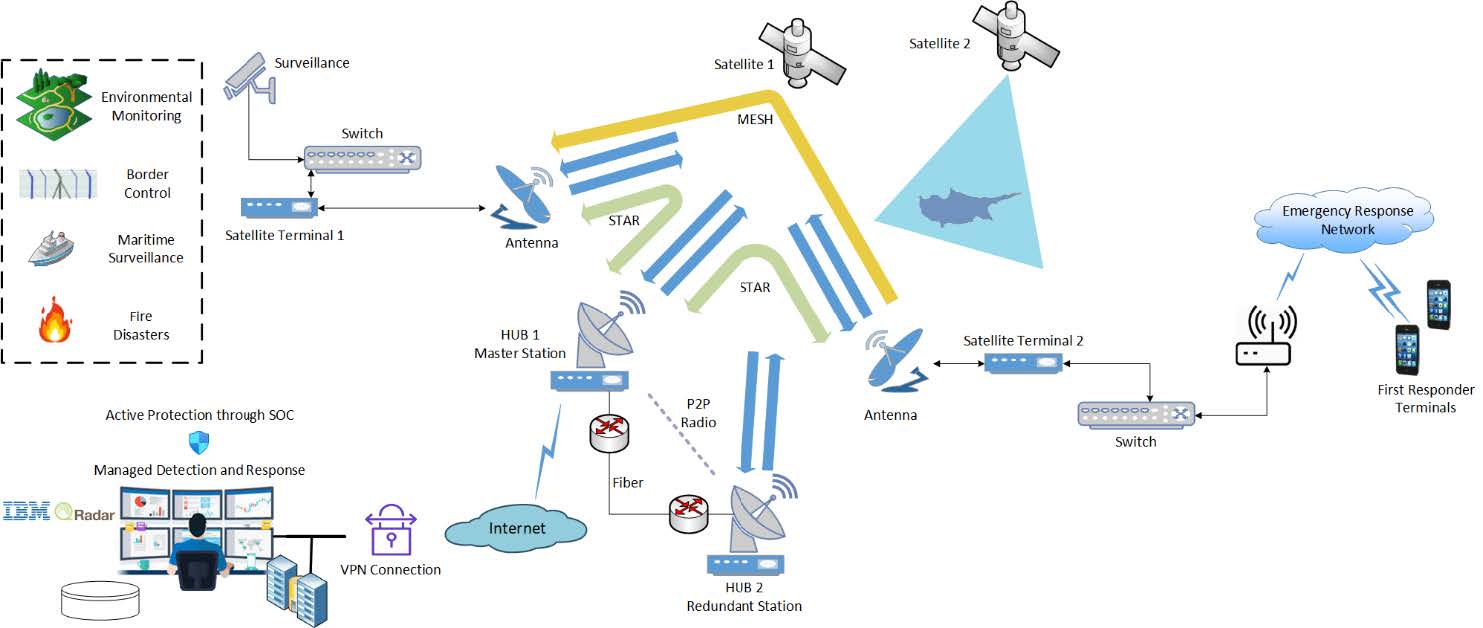
The project aims at the development of a new service, a cyber-physical platform that enhances the security over satellite public safety networks utilizing intelligent algorithms for anomaly detection, timely incident identification/notification, and efficient data routing. DEGREES will introduce new services to support crisis management through a communication framework with reinforced security and increased reliability.
The DEGREES platform consists of four main high-level components:
- The GreeCom Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
- The GreeCom Cloud
- The GreeCom Network orchestrator
- Satellite Network
The value of DEGREES solution is highlighted by considering a use case, where a set of satellite-enabled services is offered, i.e.:
- Static or mobile (UAV-supported) data/streams from conventional cameras,
- Static or mobile (UAV-supported) data/streams from hyperspectral cameras,
- Static or mobile (UAV-supported) data/streams from thermal cameras,
- Data/measurements from crossing sensors and detectors.
- Voice-video communication with the backend.
The set of services is offered for provision of enhanced situational awareness at a challenging and/or remote environment, more specifically for border monitoring and control, management of refugee flows, and respective rescue operations.
The data are gathered from the sources through wired or wireless connections at multiple portable satellite terminals deployed in the region of interest (the area of the incident) and forwarded to the system backend.
However, the described setup exposes a large attack surface to potential malicious users with the objective to undermine its operation or intercept data and communication. It should also be noted that the platform may operate in a hostile environment with many possible enemy actors in its proximity. More specifically, the cyber-attacks may compromise:
- Availability of the communication paths
- Integrity of transmitted data
- Integrity of processed data
- Confidentiality of transmitted data
- Assault system non-repudiation
DEGREES has the objective to introduce a service able to support the satellite platform in satisfying the aforementioned security requirements. The DEGREES platform treats three of the call objectives on the GreeCom Ground Segment, namely (and in priority order):
- Cybersecurity
- Data routing and communication interface
- Public safety center for disaster management
COST ACTION CA20120
NEoteRIC’s primary objective is the generation of holistic photonic machine learning paradigms that will address demanding imaging applications in an unconventional approach providing paramount frame rate increase, classification performance enhancement and orders of magnitude lower power consumption compared to the state-of-the-art machine learning approaches.
NEoteRIC’s implementation stratagem incorporates multiple innovations spanning from the photonic “transistor” level and extending up to the system architectural level, thus paving new, unconventional routes to neuromorphic performance enhancement.
All-optical implementation of powerful non-von Neumann architectures such as Reservoir Computing, Recurrent Neural Networks, Deep Neural Networks and Convolutional Neural Networks simultaneously by the same photonic chip
The Inclusive Radio Communications (IRACON) concept defines those technologies aimed to support wireless connectivity at any rates, for any communicating units, and in any type of scenarios. The Wireless Internet of Things beyond 2020 will require revolutionary approaches in Radio Access technologies, networks and systems. Some theoretical foundations have to be revisited and breaking technologies are to be discovered during the coming decade. This COST Action aims at scientific breakthroughs by introducing novel design and analysis methods for the 5th-generation (5G) and beyond-5G radio communication networks. Challenges include i) modelling the variety of radio channels that can be envisioned for future inclusive radio, ii) capacity, energy, mobility, latency, scalability at the physical layer and iii) network automation, moving nodes, cloud and virtualisation architectures at the network layer, as well as iv) experimental research addressing Over-the-Air testing, Internet of Things, localization and tracking and new radio access technologies. The group of experts supporting this proposal comes from both academia and industry, from a wide spread of countries all over Europe, with the support of some non-COST institutions and R&D associations and standardisation bodies worldwide.
Link: http://www.iracon.org
Completed Projects
GreeCom is the enabler of the Hellenic government satellite communications infrastructure that connects the country’s decision centres and authorities with voice and data services, with the goal of seamless and uninterrupted service even in times of crisis. In this context, there is a clear requirement for secure, resilient and reliable satellite communications.
The SMART project targets the design, development, integration and operational verification of a holistic user and resource communication service manager platform. The SMART solution is envisioned as a web application tool, which enhances GreeCom resilience, performance and security with the following functionalities:
- Data network management and provisioning.
The system provides the basic set of services of an application-specific customer management platform. The specific module provides the service provisioning choices and packages, handles the demand requests, retains service profiles and health status, keeps the analytical history of the user, or administrator requests and responses, keeps service/user statistics and finally has the ability to generate relevant reports.
- Bandwidth/Capacity resource planning and allocation.
The specific SMART module handles bandwidth requests, i.e., the user requests contiguous spectrum segments and provides information about the equipment and intended use. The SMART platform will have the exact view of the available and occupied resources. The overall managed bandwidth will be divided into two allocation pools: the fixed and the dynamic pool. The fixed pool includes long term leases – where the service provider has limited automated reconfiguration capabilities. On the other hand, the dynamic pool will be managed with real-time frequency planning and assignment, i.e., each request will be authenticated, examined and verified in respect to the available user equipment and based on usage history, and finally, a properly selected spectrum segment will be dynamically allocated to the user.
- Spectrum and resource analysis using the Software Defined Radio (SDR) paradigm.
An SDR is a radio system that uses generic and simplified RF hardware, while the communication components that synthesize or analyse in the waveform are implemented exclusively on software – executed on embedded system and/or a conventional computer. In the SMART, SDR is used to implement a radio resource monitoring tool, in a time-frequency grid, that uses detection algorithms in order to: identify transmissions; classify them as licensed or unlicensed transmissions and estimate some signal features; and finally identify bandwidth segmentation, as well as monitor the resource utilization.
- Optimized resource scheduling and allocation.
This component evolves the SMART platform from a management software to an automated and optimized resource allocation engine. In this context, the user requests dedicated throughput instead of specific spectrum segment. The system, in real-time will estimate the performance and select the optimal bandwidth allocation strategy that covers the user requirements and optimizes the overall system spectrum efficiency.
- Automated ground segment control and monitoring
This element of SMART project will close the loop of automation and hereby create an agile and resilient system. The results of the optimized resource scheduling and allocation will be translated into a setting of the according ground station equipment. The equipment will be monitored and remotely controlled in order to adjust the device settings as it is required for a dynamic reallocation of resources.
- A study on the definition of use cases addressed by a future Greecom network expansion and the technical requirements for the expansion will run in parallel to the SMART project objectives.
Following the increasing demand for satellite communication and earth observation capabilities the interest in Low Earth Orbit solutions has increased. Being able to utilize its own constellation of LEO satellites Greece can acquire a significant advantage, as it becomes independent of acquiring such data from third party providers, as well as enabling the ability of using a specialized payload, designed from the ground up to serve the type of observations needed in the needed satellite overpass frequency.
The SMART platform will provide proper interfaces towards users as well as third party applications – in order to provide extendable and scalable features.
The SMART platform is expected to have major impact into the GreeCom ecosystem since:
- It develops new capabilities: With the use of efficient management, satellite resource allocation, monitoring and control of satellite communication capabilities, the achievement rate of the Governmental objectives will also increase. The efficient and reliable allocation of satellite resources at a national level is welcome by both military and civilian authorities – especially since it can effectively coordinate their co-existence. Furthermore, it will lead all the involved governmental stakeholders to consider new solutions to exploit the dynamically available satellite resources.
- It eliminates distrust by governmental authorities. The reluctance of the different Governmental entities to cooperate in shared efforts/resources programs could be overcome through a centralized architecture which will implement joint plans for investment, exploitation and allocation of resources. In this way the fragmentation of efforts could be minimized and goals could be more efficiently be achieved.
- It plays the role of the driver for future needs. The efficient monitoring of the allocated resources would be the driver of any future needs. The limitations that the current allocations impose to entities’ missions can help identify the requirements for furtherly expanding the current capabilities mitigating the current availability risks
- It provides an accurate record guiding and harmonizing new investments in the domain. The system keeps accurate history and records of requests, allocations, system exploitation and resource utilization. These reports could guide the actions for any new expenditure for satellite related equipment, either on the ground or in orbit, aligning any capital expenditure with the current national strategy.
- It creates new opportunities for beyond the national border’s cooperation. At an international level, a resilient, dynamic and, where possible, automated management framework allows two or more countries to use their allocation systems to jointly coordinate and share satellite resources, supporting each other in emergency (or not) situations. Joint resource management could be carried out with the exploitation of the SMART system that utilizes appropriate parameters and criteria based upon the situation in need.
- It supports the satellite communications as field and solution. Based on the GreeCom experience, the use of satellite resources can be enhanced through efforts mutually conducted by the various Governmental entities. In order to achieve that level of cooperation, technical means are required which will efficiently manage and monitor the satellite resources among the various stakeholders.
The final objective of SMART is the definition of use cases addressed by a future GreeCom expansion and the definition of the related technical requirements. The use case definition will be performed through the determination of users and stakeholders’ needs. The definition of scenarios of the high-level system architecture, the trade-off of satellite configuration, the spectrum requirements analysis within the limits imposed by the Radio Regulations and the identification of regulatory challenges are the main objectives to be reached towards the future GreeCom expansion design.
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is a state of a cognitive performance below of what is expected for an age and an educational level, but above a pathological level. MCI is one of the early symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease characterized by significant memory impairment that does not, however, meet the criteria for dementia. MCI patients may forget important information previously recalled, such as meetings, conversations, or recent events but continue to exhibit normal functional activities. MCI is also linked to the impairment of other aspects of cognitive function, such as attention, language, visual or executive function, including the inability of a person to make the right decisions, judge the time or sequence of steps required to fully execute a complex task.
Long-term studies show that on a global scale 15-20% of people aged 65 and over may develop MCI. Besides ageing, a wide spectrum of diseases and clinical conditions are related to MCI. In the case of cardiovascular diseases (stroke, heart attack, etc.), in addition to motor deficiency, patients develop cognitive and affective disorders. The relation of MCI to Parkinson’s disease has been similarly examined. Aphasia, a non-amnestic single cognitive domain MCI, does not affect memory and patients still reason as normal but are unable to communicate their thoughts easily.
Given the increase of the proportion of older people in the world population as well as the sharp increase in the survival rate of patients with acute diseases which, however, affect their cognitive functions, the importance of developing MCI prevention and rehabilitation tools is obvious. In recent years the interest in cognitive rehabiliation has led to the discovery of pathogenetic mechanisms of cognitive impairment and the development of new approaches to the recovery of neurons of the brain.
To this end, neuropsychologists are now increasingly using information and communication technologies, including serious games. Digital applications can provide a great alternative with respect to traditional methods, as they allow the patient to practice cognitive functions with rich media, such as sounds and images. A rehabiliation tool capable of managing such types of training material can generate different and operative experiences supporting the recovery process of the patient, while also recommending novel exercises that are difficult to realize with hard copy approaches.
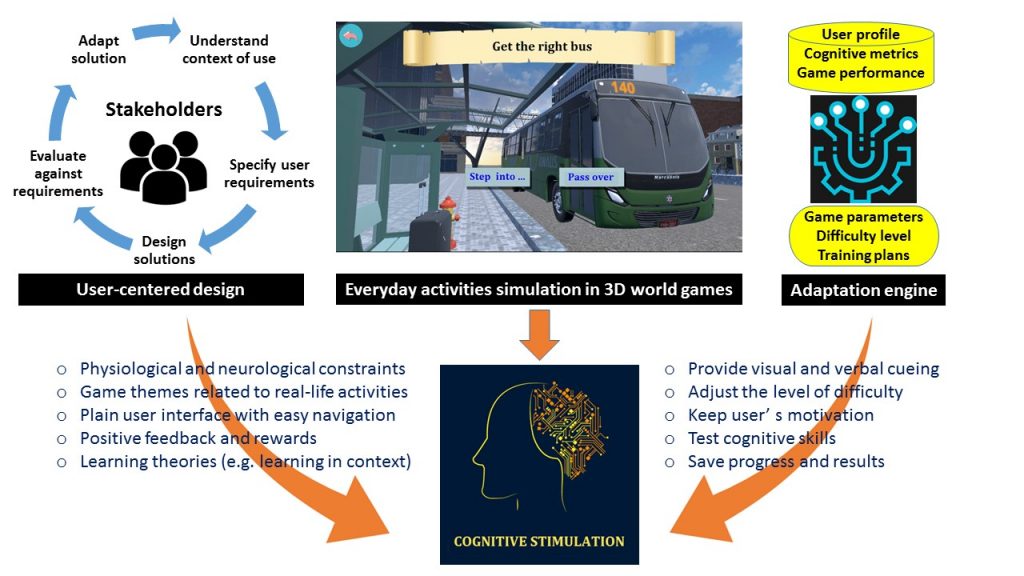
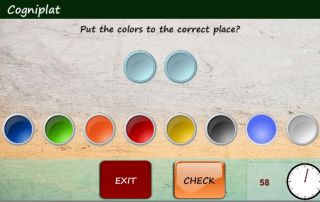
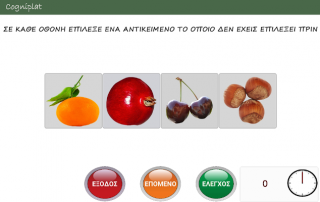
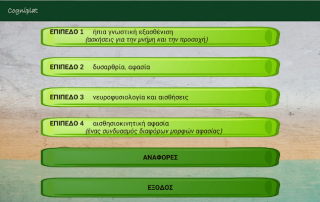
The COGNIPLAT platform is an innovative cognitive impairment rehabilitation tool that is developed for assisting elderly who have MCI but have not yet developed dementia. It is built based on a multi-disciplinary approach combining theories of neuropsychology, cognitive linguistics and speech therapy organized in five domains, one diagnostic and four training domains focused on enhancing cognitive functions through different game exercises. In addition, the platform is designed to automatically adjust the complexity and type of exercises by adapting the cognitive requirements of the games to the characteristics of each patient.
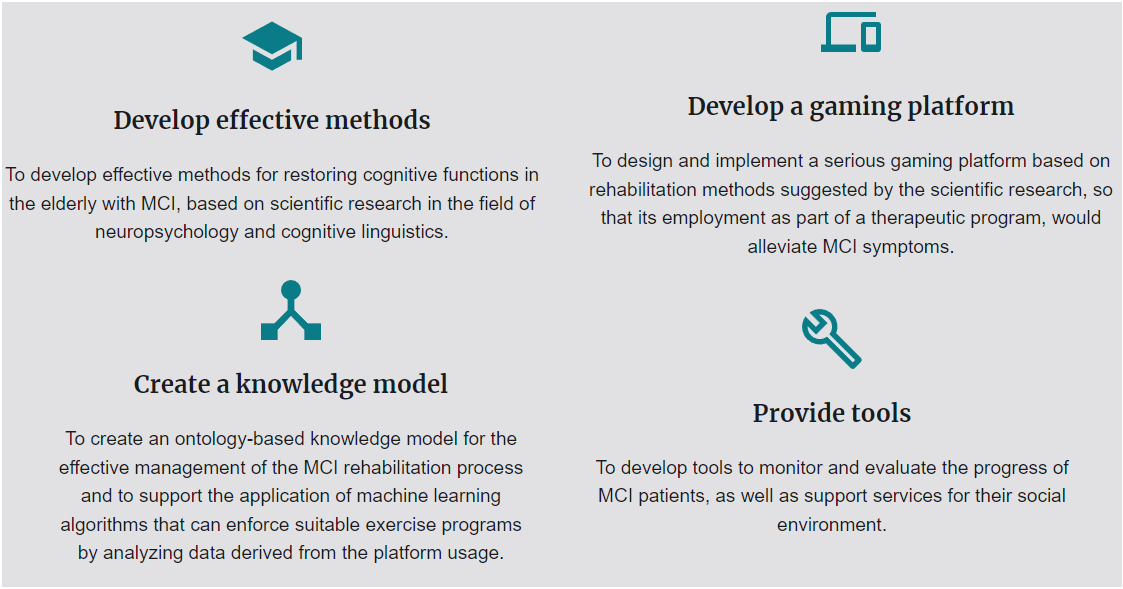
Objectives
The Platform
The COGNIPLAT platform is an innovative cognitive impairment rehabilitation tool that is developed for assisting elderly who have MCI but have not yet developed dementia. It is built based on a multi-disciplinary approach combining theories of neuropsychology, cognitive linguistics and speech therapy organized in five domains, one diagnostic and four training domains focused on enhancing cognitive functions through different game exercises. In addition, the platform is designed to automatically adjust the complexity and type of exercises by adapting the cognitive requirements of the games to the characteristics of each patient.
The diagnostic domain aims to evaluate, through a specific set of exercises, the degree of impairment of the patient’s cognitive functions in order to determine the difficulty level of the exercises to start.
The remaining areas focus on the reinforcement of different cognitive functions through exercises.
The first cognitive domain is focusing on memory and includes exercises that focus on recalling the position of objects and patterns, a sequence of numbers, elements of associative knowledge etc.
The second cognitive domain focuses on attention with the use of exercises that request, for example, to replace words or phrases with images or image sequences and identifying objects displayed on the screen.
The third cognitive domain focuses on enhancing the perception ability with the use of exercises that require some kind of orientation or determining the location of an object with respect to another.
The fourth cognitive domain focuses on reasoning and problem solving with exercises such as solving arithmetic crosswords and selecting the right pattern to reasonably complete a given sequence.
In addition, the platform includes the implementation of game scenarios based on interactive 3D environments with activities from everyday
COGNIPLAT Application
Home Activites
For further information, please visit https://cogniplat.aegean.gr.
Greenet is an Initial Training Network (ITN) Marie Curie project that is focused on the analysis, design, and optimization of energy efficient wireless communication systems and networks.
- Recruitment of talented Early Stage Researchers (ESRs) with the objective to conduct top-notch research.
- Develop personalised training and career plans.
- Allow the ESRs to understand and address key research challenges on energy efficient communications.
- Offer to each ESR top-level training and research programs with the twofold objective to reinforce and corroborate their own background, as well as to complement this with active participation in a multi-disciplinary network of research scientists.
- Complement the typical competences of “applied research” with “complementary” activities.
- Guide and help the ESRs to build the bridge from academia to a remarkable and impactful professional career in either the private or public sectors.
IC1004 is the Action on Cooperative Radio Communications for Green Smart Environments and belongs to the ICT Domain. This Action addresses research issues in the field of cooperative radio communications to make our society cleaner, safer, and more energy efficient.
Action’s goals are:
- to increase knowledge of cooperative communications applied to Green SEs (GSEs), by exploring and developing new methods, models, techniques, strategies and tools, in a context enriched by deep industry-academia links;
- to play a supporting role to European industry, by ensuring all Working Groups are focused toward aspects of interest to industry;
- to train young researchers in the field of cooperative radio communications for GSEs, via annual training schools.
Link: http://www.ic1004.org
Virtualised service platforms and cloud computing hold great promise for delivery of large applications in e-Government. However, to date, the fundamental shared-resource nature of virtualisation technologies has raised legitimate security concerns for Government and other organisations with duties to protect confidential data. The PASSIVE project proposes an improved model of security for such virtualised systems which includes:
- A policy-based Security architecture, to allow security provisions to be easily specified, and efficiently addressed.
- Fully virtualised resource access, with fine-grained control over device access, running on an ultra-lightweight Virtual Machine Manager.
- A lightweight, dynamic system for authentication of hosts and applications in a virtualised environment.
In so doing, PASSIVE will lower the barriers to adoption of virtualised hosting by government users, so that they may achieve the considerable gains in energy efficiency, reduced capital expenditure and flexibility offered by virtualisation.
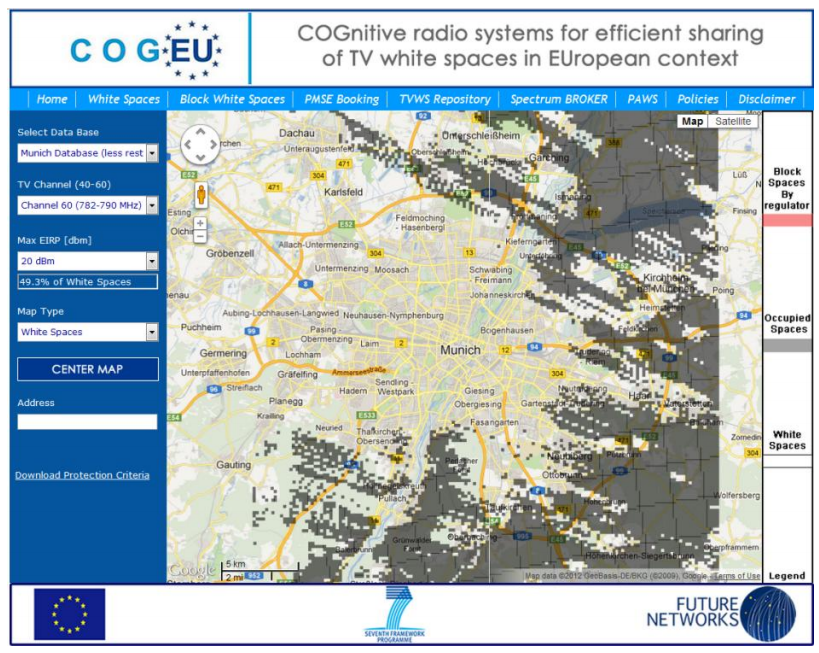
The COGEU project is a composite of technical, business, and regulatory/policy domains, with the objective of taking advantage of the TV digital switch-over (or analog switch-off) by developing cognitive radio systems that leverage the favorable propagation characteristics of the TVWS through the introduction and promotion of real-time secondary spectrum trading and the creation of new spectrum commons regime. COGEU will also define new methodologies for TVWS equipment certification and compliance addressing coexistence with the DVB-T/H European standard. The innovation brought by COGEU is in the combination of cognitive access to TV white spaces with secondary spectrum trading mechanisms in a real demonstrator.
Link: http://www.ict-cogeu.eu
HURRICANE aims to provide concrete networking system answers to the question how an optimized handover operation is performed between two cooperative RATs that constitute potential business cases for both Telecom Operators and Broadcasters in the context of a FMC communications environment. The main objectives of the project are to Investigate, design, implement, validate, and propose for standardisation inter-system handover operations among radio cooperative networking environment.
COST2100 is the Action on Pervasive Mobile & Ambient Wireless Communications and belongs to the ICT Domain. This Action basically addresses the various topics that are currently emerging in the area of mobile and wireless communications and was proposed by the group of researchers who participated in the previous COST Actions on mobile communications. The main objective of this Action is to increase knowledge of mobile and wireless network technologies, by exploring and developing new methods, models, techniques, strategies and tools that will facilitate the implementation of next generation mobile radio communication systems and will foster the development of the paradigms of pervasive and ambient wireless communications.
Link: http://www.cost2100.org
The main objective of the project is the design, the optimization and the experimental evaluation in a test-bed of advanced MAC protocols for cooperative ARQ scenarios in order to extend the coverage area of NGNs infrastructure networks (WiMax/UMTS LTE or WLAN) and evaluate the performance of the propose protocol in different cooperative schemes and different network conditions.
Link: https://cordis.europa.eu/project/rcn/88370/factsheet/en
The renown beyond 3G scenario depicts a diverse wireless networking world of network-of-wireless-networks accommodating a variety of radio technologies and mobile service requirements in a seamless manner. The achievement of this vision raises significant research challenges in view of system coexistence; system scale; network robustness requirements; and evaluation tool design to provide a framework for cost-effective assessment of optimisation algorithms within a heterogeneous system environment. The UNITE platform aims to address the aforementioned research challenges by: (a) implementing an efficient, accurate and scalable Virtual Distributed Testbed (VDT) to support cross-system, and cross-layer optimisation of heterogeneous systems in a unified manner. (b) Through the use of the virtual testbed, to investigate, design and evaluate cross-layer and cross-system interactions, between next generation radio and protocols without neglecting important real-system details.
Link: http://www.ist-unite.org
Design and development of telemedicine services to serve the needs of the inhabitants of the region, focusing on situations of emergency medical care. Services will be based on technologies that enable the collection and transmission of important diagnostic biosignals (ECG, blood pressure, pulse oximetry, temperature), the collection and transmission of video signals or image sequences. Services include diagnosis, medical support in long distances and counseling services in remote medical units (ambulance, rural health centers, provincial doctors, etc.) by specialists at regional hospitals or medical centers.
The goal of the INHOME project is to provide the means for improving the quality of life of elderly people at home, by developing generic technologies for managing their domestic ambient environment, comprised of white goods, entertainment equipment and home automation systems with the aim to increase their autonomy and safety. Contrary to the practises followed up to now, the INHOME project focuses on the problem of appliances flexible use by discriminating between experienced and inexperienced rather than enabled or disabled users. By adopting this radically different standpoint the project is posed to set out a generic set of appliance design guidelines targeting the intensification of home appliances use and user dependency. In accordance with this concept, the INHOME project aims at furnishing its offerings through the establishment of the four-tier architecture. The bottom line technology is offered by the ESTIA project (IST-FP6-4-27191), which focuses on the design and development of technologies for efficient personalised management of audiovisual content and white goods functions, locally within the home.
Link: https://cordis.europa.eu/project/rcn/93621/factsheet/de
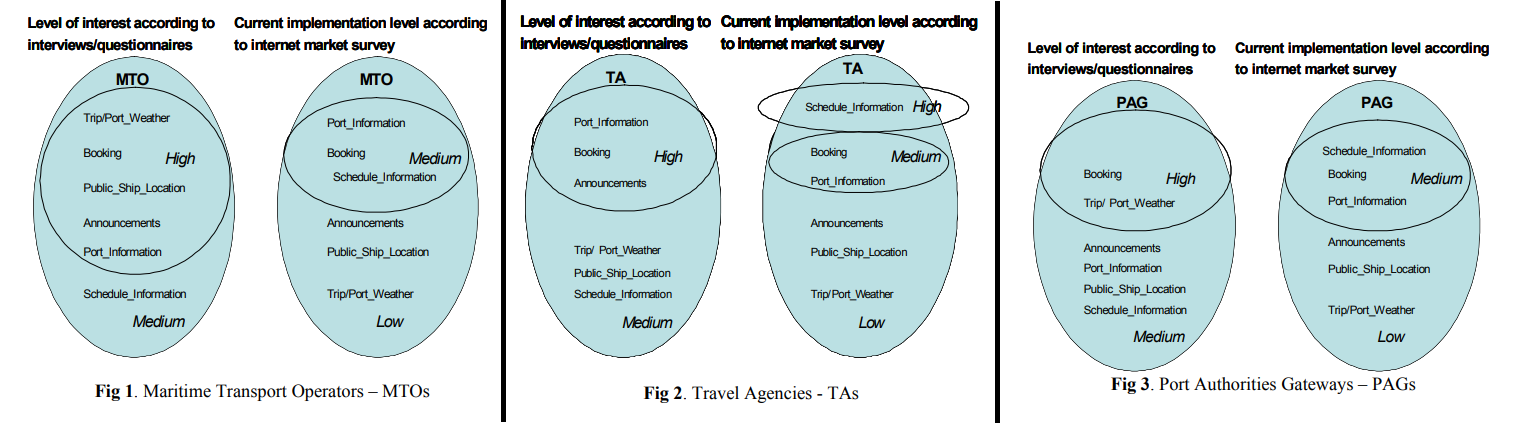
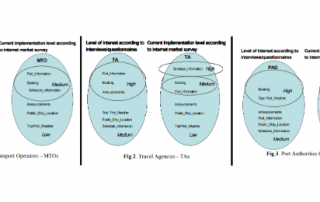
TeleSHIPping is a market validation study of an information service for travellers and tourists on board ferries/ cruisers. This is based on an innovative service platform that enables secured links and interconnections among all the market players in the service provision chain (eg. Application service providers, vessel operators, port/sea/traffic monitoring/state-city authorities, travel agents and tour operators, computerised reservation systems, tourism content providers etc.), while offering the access to a variety of services for the general public. The major objective of the TeleSHIPping project concerns a market validation study to investigate:
- The commercial feasibility of an internet/intranet based information system for ferry and cruise passengers, for shipping lines, for port authorities, and for travel agencies.
- The adequacy of available modern communication technologies for structuring the project’s serving platform enabling information exchange among interested parties pre-trip or during trip.
- The implementation of a series of alternatives for the services delivery to the general public, identifying the potential advantages and disadvantages and profitable opportunities associated with them.